Tig welding can produce beautiful-looking welds, and more importantly, x-ray quality deposits on some of the most critical welding applications. For the beginner, it may be a very intimidating process. Selecting the right tungsten (type and size), cup size, and shielding gas and gas flow can be a daunting task. Below is a quick guide for selecting the right items for your tig welding. This is basic setup information, if you have questions please leave it in the comments sections.
Shielding Gas – 90% of applications can be done with 100% argon. Carbon steel, stainless steel and aluminum can all be welded using pure argon shielding gas. Argon/Helium mixes are sometimes used to provide a hotter arc. This helps in welding aluminum and copper alloys. These materials have high thermal conductivity and the added helium makes for easier and faster starts.
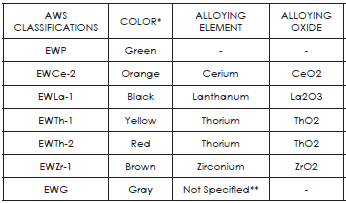
Tungsten Type – Tungsten used for tig welded is usually alloyed with different elements to achieve different characteristics. Once again, for simplicity, all you need is to have pure tungsten (for aluminum) and either thoriated or created tungsten (for steel and stainless). Tungsten for tig welding is color coded. Pure will have a green band in one of the ends. Thoriated will be red and created will be orange. The chart below shows other alloys found in tungsten.
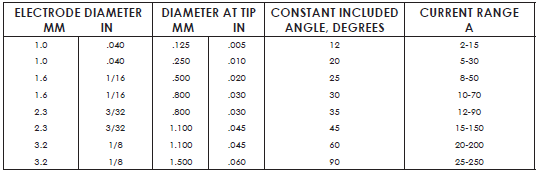
Tungsten Size – The size of your tungsten will depend on the application. Mainly on the material thickness and the amperage needed to achieve a proper weld. Thicker materials will require more current and thus bigger tungsten. For beginners, it’s recommended to stick with a 3/32” diameter tungsten. See the chart below for current ranges of all sizes.
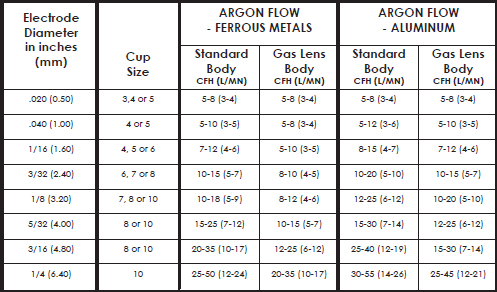
Gas Flow – Most people learn to weld using the GMAW (MIG) process. Adequate gas flow for GMAW typically ranges from 35 to 50 cubic feet per hour. We need a lot less flow in tig welding. A flow of 15 to 25 cfh will cover most applications. Very large cup sizes will require more flow, but for the apprentice using about 20 cfh is sufficient. See the chart below for recommended flow rates.

Polarity – This is simple. Use DCEN (DC Electrode Negative is also referred to as Straight Polarity or simply DC-) when welding steel and stainless steel. Use AC (Alternating Current) when welding aluminum and magnesium. Don’t ever use DC+ (DCEP) as it will burn up your tungsten in a heartbeat.



