What are the lateral oscillation methods of manual tungsten arc welding torches? What are the characteristics of each?
In many cases, a small lateral oscillation of the torch is required in order to obtain a wider weld path or to ensure a good fusion on both sides of the bevel. The frequency and amplitude of the oscillation are based on the principle of not destroying the protective effect of the molten pool. There are three common forms of oscillation: r-shaped oscillation, arc zigzag oscillation, and arc zigzag side shift oscillation.
①r-shaped oscillation
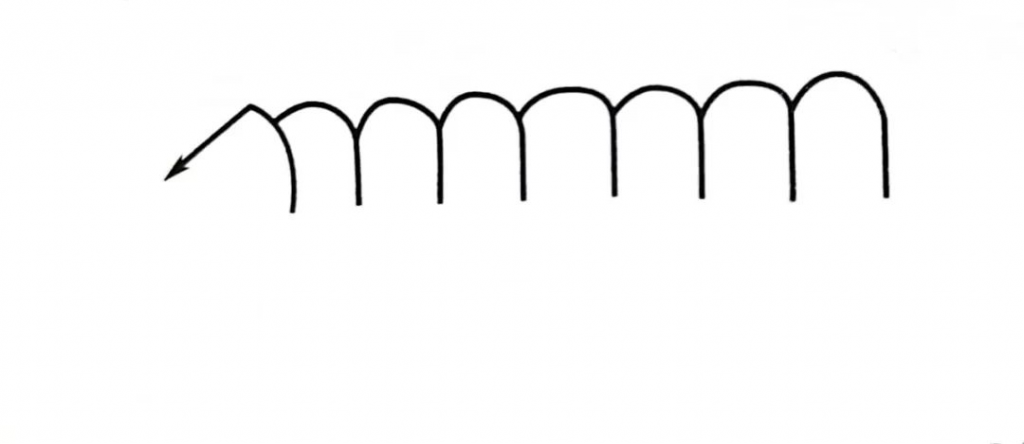
The lateral oscillation trajectory of the welding torch is approximately r-shaped, and this method is mainly used for butt joints of unequal thickness. When welding, the torch in the r-shaped movement at the same time, so that the arc is slightly biased toward the thick plate, and make the arc in the thick plate on one side to move slower or to make a suitable stay, in order to control the degree of melting on both sides, to prevent the thin plate burn through the thick plate is not welded through.
②Circular arc zigzag swing
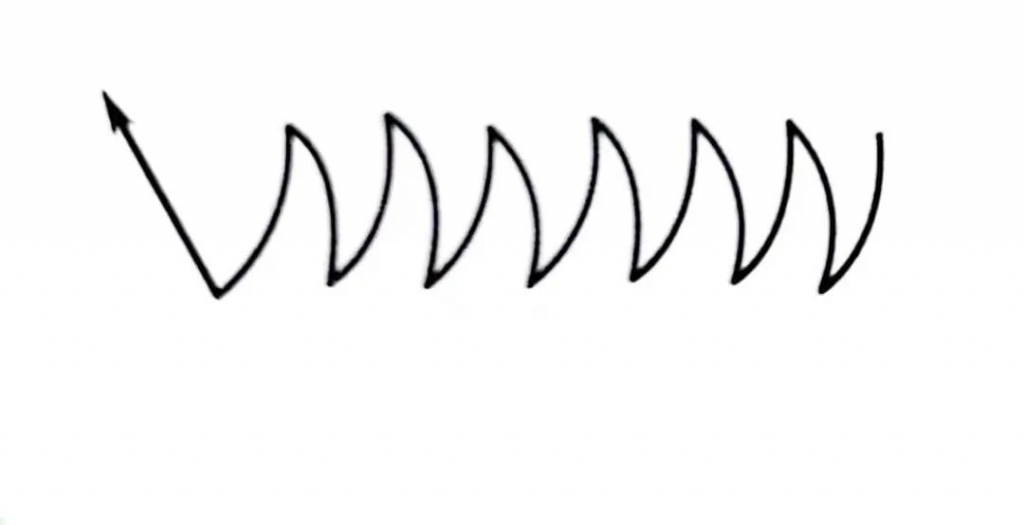

Subscribe to DeepL Pro to translate larger documents.As the name implies, the trajectory of the torch is in the shape of an approximate circular zigzag. This method is suitable for large T-shaped joints, lap joints of thick plates and butt joints of medium-thick plates with open bevels. When welding, the torch slows down or stays slightly on both sides of the weld, and the movement speed can be accelerated when passing through the center of the weld, so as to obtain a well-formed weld.
③Circular arc zigzag side shift swing
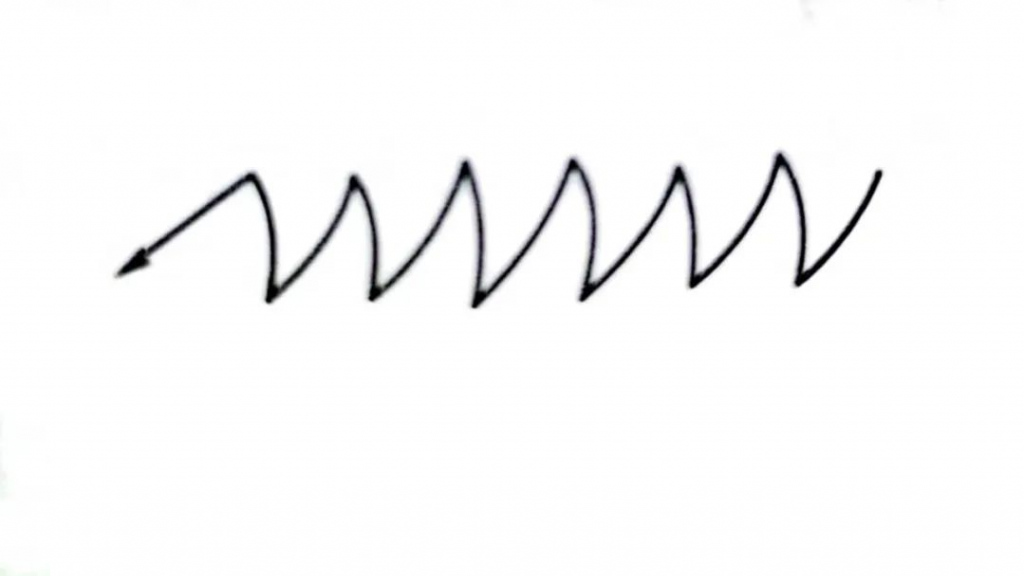

The trajectory of the torch is circular and moves forward in an oblique zigzag shape, which is mainly used for uneven corner joints. When operating, the torch is biased toward the protruding part, and the torch makes a circular arc zigzag sideways movement so that the arc stays in the protruding part for an increased time to melt the protruding part, without or with less filler wire.
When the welding gun swings, the wire fed also needs to swing, and the swing amplitude of the two should be consistent with each other.


